Energy Saving for Pump and Fan
Energy Saving for Pump and Fan
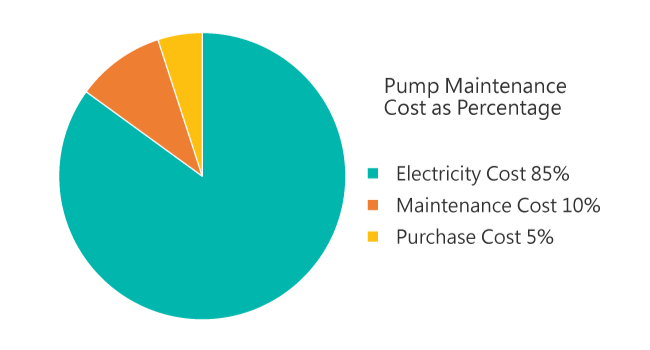
Pumps and fans are machines used to transfer fluids and gases and consume a significant amount of energy. They are widely used in air conditioning, sewage disposal, heating systems, and booster systems. According to statistics, the electricity energy consumption of pumps and fans reaches 20% globally. Applying variable frequency control can reduce energy consumption by 30% to 50%.
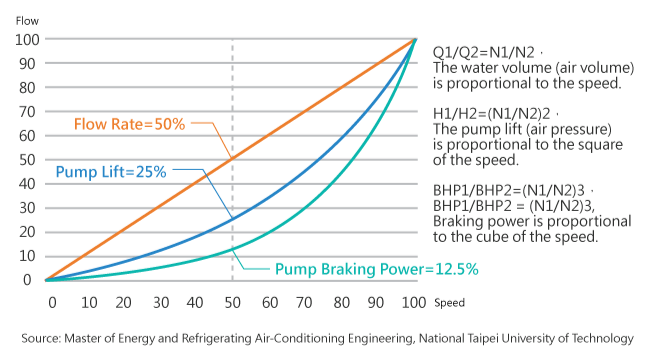
Affinity laws
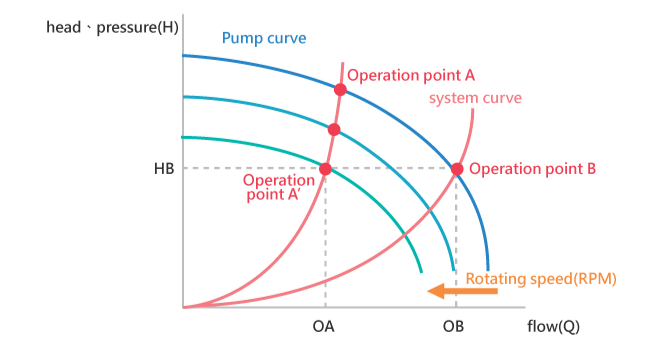
Pump curve
Applying a drive to reduce the speed of the pump. The intersection point of the system curve and pump curve will move, and we obtain the operating point where pump flow and head decrease simultaneously. Due to the affinity laws, power is greatly reduced.
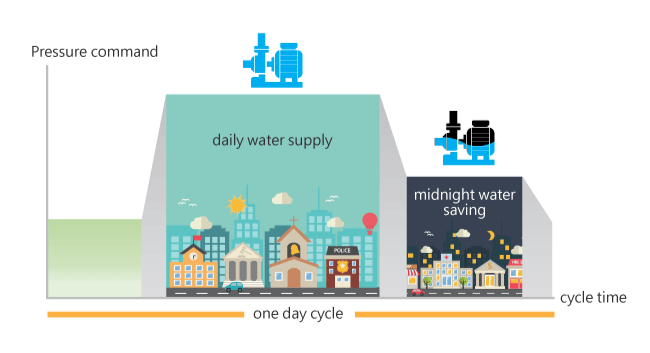
Smart period constantpressure adjustment
Applications
-

The Constant-PressureWater Supply System
-

The Constant-PressureWater Control System
-

Multiple-pumpConstant-Pressure System
-

Helicopter fans
-

Exhaust equipment
-

Exhaust fan
1. Calculation of pump power consumption
The formula for calculating the power consumed by the pump system is as follows:
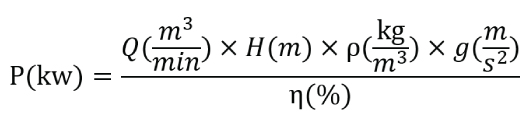
Calculation example of pump power consumption:
The specification of the constant pressure pump is:
Flow (Q)= 6(m3/min), Head (H)= 50(m), Pump Efficiency (η)= 85%, Fluid Density (ρ)= 1(kg/m3)
Gravitational Acceleration (g) = 9.81 (m2/s), the total annual operating hours (T) = 6000 (hrs)
According to the formula, the power consumption of the pump operation is about 57.5kW.
2. Inverter Control for Constant Pressure Pump
If the required flow rate is halved, the required head will not change.
The flow rate is reduced from Q=6(m3/min) to Q=3(m3/min), using frequency inverter control, according to the calculation formula, the power consumption of the pump operation is reduced to 28.8kW, and the energy saving rate is about 50%.
Pdiff(kW)=P1-Pfrequency inverter control=57.5kW-28.8kW=28.7(kW)
The difference of reduction in electricity charges (per year) (electricity bills are calculated at 2.7 NTD per kWh):
Electricity bill=28.7kW×6000hrs×2.7 NTD/kWh=464,940(NTD)
Therefore, by using the frequency inverter to control the pump motor, when the system flow is reduced, the annual electricity bill will be reduced by 464,940NTD.

